

.png?sfvrsn=1b6bae1a_0) (FASTER)
(FASTER).png?sfvrsn=ac211bda_0)
The need for reliable, accurate, and portable BTEX sensors is driven by the harmful effects of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on human health and the environment. BTEX compounds are commonly found in emissions from industrial processes, transportation, and fuel combustion. Traditional methods struggle with selectivity due to the similar molecular structures of BTEX species, which this laser-based system successfully addresses through the use of advanced neural networks.
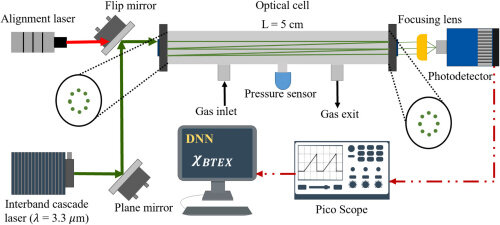
Optical schematic of BTEX sensor
The sensor operates near 3.3 µm, targeting the C-H stretching bands of BTEX species. The use of DNNs enhances the selectivity by distinguishing overlapping spectra. The system combines laser absorption spectroscopy (LAS) with an off-axis cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy (CEAS) setup, achieving high sensitivity for trace detection. The sensor has been validated in real-time tests and shown excellent performance in distinguishing multiple BTEX components.
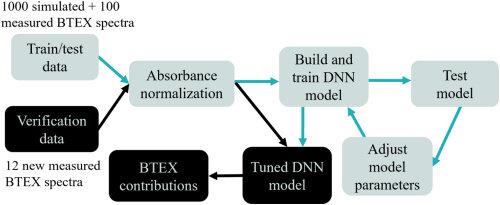
Schematic for the overall process to build the DNN model and to extract BTEX
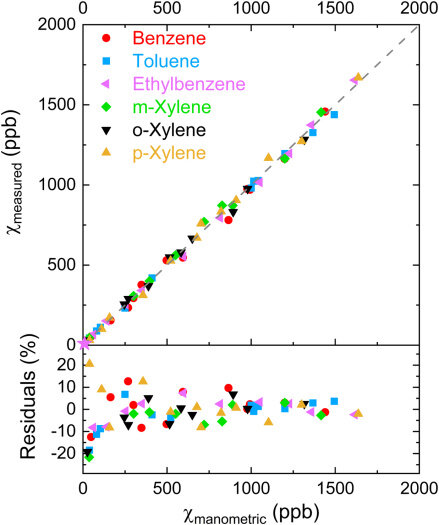
Comparison of experimentally measured and manometric mole fractions of BTEX

Saudi Aramco – Environmental Protection
Patents